Muối nitrat là gì? Chi tiết lý thuyết và bài tập thực hành
Formed from the reaction of nitric acid (HNO3) with metals, nitrate salt is no longer a strange term for Chemistry lovers. Nitrate salts appear commonly not only in Chemistry exercises but also in real life. In this article, Nguyễn Tất Thành will explore this topic with you, learn what nitrate salt is, detailed theory and practice some basic exercises.
- Tiếng Việt lớp 4 học những gì? Làm sao giúp bé học tập đạt kết quả tốt?
- Gợi ý 5+ kênh youtube học chữ cái tiếng Việt từ cơ bản đến nâng cao chất lượng
- Công nghệ cao là gì? Tầm quan trọng và các ngành công nghệ cao
- Silic và hợp chất của Silic: Chi tiết tính chất và ứng dụng
- Bỏ túi các từ Tiếng Anh bắt đầu bằng chữ Y – Bản đầy đủ nhất
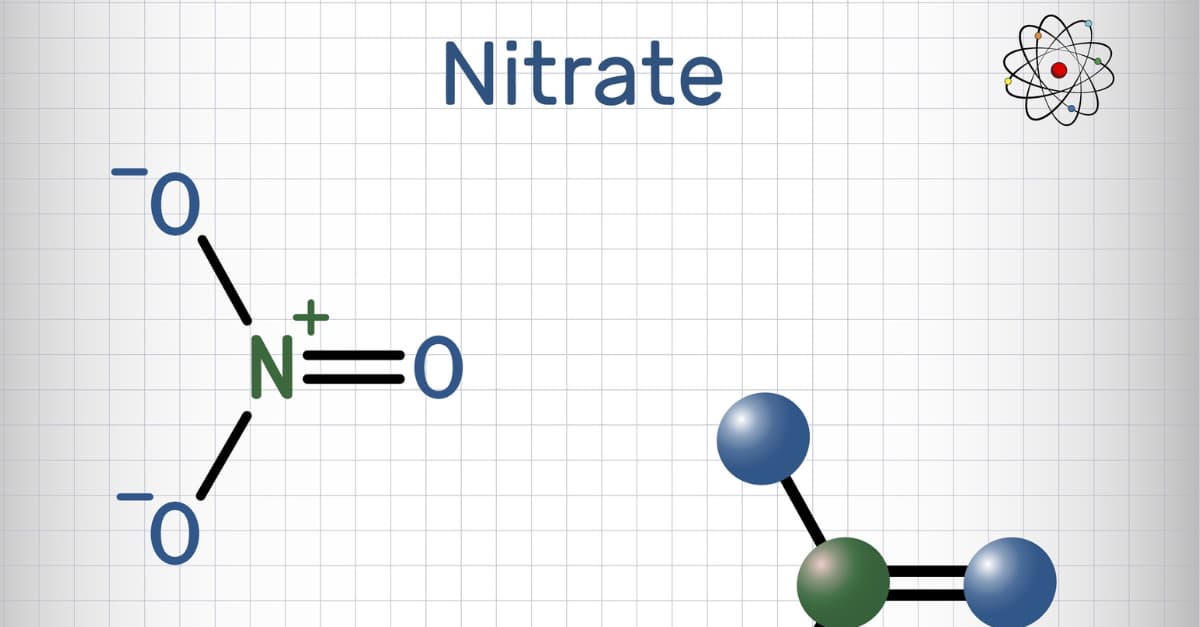
What is the definition of nitrate salt?
Concept: Nitrate salt is a salt of nitric acid. It is composed of nitrate ion NO3– and positive metal ions. Typically, nitrate salts are formed by reactions of nitric acid with metals. In addition, it is also produced by other positive ions such as NH4+.
Bạn đang xem: Muối nitrat là gì? Chi tiết lý thuyết và bài tập thực hành
For example: In fact, each different type of nitrate salt possesses somewhat different physical and chemical properties. Some examples of common nitrate salts include: Sodium Nitrate NaNO3, Potassium Nitrate KNO3, Ammonium Nitrate NH4NO3, Calcium Nitrate Ca(NO3)2, Silver Nitrate AgNO3, Copper (II) Nitrate (Cu( NO3)2)…
General formula: M(NO3)n.
Physical properties of nitrate salts
All nitrate salts are readily soluble in water and are strong electrolytes.
They dissociate completely into ions in dilute solution:
M(NO3)n → Mn+ + nNO3-
For example: NaNO3 → Na+ + NO3-
.jpg)
Chemical properties of nitrate salts
So what are the typical chemical properties of nitrate salts that you need to remember?

Nitrate salt has the general chemical properties of salt
First of all, nitrate salt has the general chemical properties of salt. Include:
Nitrate salt reacts with acid to create new salt + new acid.
For example: Ba(NO3)2 + H2SO4 → BaSO4 + 2HNO3
Nitrate salt reacts with base solution, creating new salt + new base.
For example: Mg(NO3)2 + 2NaOH → Mg(OH)2 + 2NaNO3
Nitrate salt reacts with salt solution to form 2 new salts.
For example: Mg(NO3)2 + Na2CO3 → MgCO3 + 2NaNO3
Nitrate salt reacts with metals that have a stronger reducing power than the metal in the salt, creating a product of new salt + new metal.
For example: Cu + 2AgNO3 → Cu(NO3)2 + 2Ag
Pyrolysis of nitrate salts
Nitrate salts are easily decomposed by heat and release oxygen. This is why nitrate salts have strong oxidizing properties at high temperatures.
For example: 2KNO3 → 2KNO2 + O2(↑) (temperature)
-
Nitrate salts of medium metals (from Mg to Cu) such as zinc, iron, lead, magnesium, copper… decompose to form oxides of the corresponding metals + NO2 and O2.
For example: 2Cu(NO3)2 –> 2CuO + 4NO2(↑) + O2(↑)
For example: 2AgNO3 → 2Ag(↓) + 2NO2(↓) + O2(↑) (temperature)
Note: In some cases, pyrolysis salts do not follow the above rules, typically Fe(NO3)3, NH4NO3…
How to recognize nitrate salt?
In a neutral environment, NO3- ion does not show oxidation properties. But on the contrary, in acidic environments, NO3- ion exhibits oxidation properties equivalent to HNO3.
Thus, to identify nitrate salts in solution, people add a little copper chips and dilute H2SO4 solution to the mixture and then gently heat it. The reaction creates a blue solution, the colorless NO gas released is oxidized to reddish brown NO gas.
Equation:
3Cu + 8H+ + 2NO3- → 3Cu2+ (blue color) + 2NO(↑) + 4H20 (Condition: temperature)
2NO + O2(air) → 2NO2 (red brown)
How to prepare nitrate salt?
Nitrate salts are prepared by reacting HNO3 with metals, metal oxides, bases, and salts by ion exchange reactions (salts in which the metal retains its valence) or redox reactions (forming metal salts). with high chemotherapy).
.jpg)
Important applications of nitrate salts
What is the application of nitrate salt? Nitrate salt has many important applications in practical life. And, each different type of salt has its own properties and applications.
.jpg)
-
Sodium nitrate salt (NaNO3): Most commonly used in chemical fertilizers (nitrogen fertilizers) in agriculture, along with NH4NO3, KNO3 and Ca(NO3)2. Besides, it is also used in making gunpowder, used to produce nitric acid – one of the most important chemicals. In addition, it is also used with potassium nitrate salt as a preservative, applied in wastewater treatment technology…
-
Potassium nitrate salt (KNO3): A prominent application of Potassium nitrate is making black explosives with 75% KNO3, 10% S and 15% C. Potassium nitrate salt is also used as fertilizer for plants, food preservation, Prepare oxygen and nitric acid, use as additives in food, toothpaste…
-
Ammonium nitrate salt (NH4NO3): Used in the production of explosives, fertilizers, titanium ore processing, N2O production, anhydrous ammonia preparation,…
-
Calcium Nitrate Ca(NO3)2 Salt: Raw material for fertilizer production and used as a concrete additive in construction. Rubber production, applications in wastewater treatment, room cooling, solar energy storage… are also outstanding applications of Calcium Nitrate.
See more:
4 common forms of nitrate salts you should know
Nitrate salts appear commonly not only in high school chemistry exercises but also in real life. Below are the 4 most common forms of nitrate salts that you should know.
.jpg)
Sodium nitrate salt (NaNO3)
Sodium nitrate salt is one of the most commonly occurring nitrate salts.
Chemical formula: NaNO3.
Physical properties:
-
Appearance form: Crystal or white powder. No color and slightly sweet taste.
-
Soluble well in water and liquid ammonia, slightly soluble in alcohol solutions, easily decomposed.
-
Xem thêm : Hợp kim của sắt: Gang, thép là gì? Phân loại và cách sản xuất
Density: 2.257 g/cm3.
-
Melting temperature: 308 degrees Celsius.
-
Boiling temperature: 380 degrees Celsius.
Chemical properties:
-
Easily decomposed at high temperatures. The products produced are sodium nitrite and oxygen.
-
Reacts with some acids. The products created are new salt + new acid (in the exchange reaction), gas and water (in the redox reaction).
Potassium nitrate salt (KNO3)
Besides, one of the other extremely popular nitrate salts is Potassium nitrate with unique physical and chemical properties.
Chemical formula: KNO3
Physical properties:
-
Appearance form: Solid, white and odorless.
-
KNO3 is highly soluble in water, but slightly soluble in alcohol-containing solutions such as ethanol. Solubility increases proportionally to water temperature.
-
Melting temperature: 334 degrees Celsius
-
Boiling temperature is 400 degrees Celsius.
Chemical properties:
For example: S + 2KNO3 + 3C → K2S + N2 + 3CO2
For example: 6FeSO4 + 2KNO3 (condensed) + 4H2SO4 → K2SO4 + 3Fe2(SO4)3 + 2NO + 4H2O
Ammonium nitrate (NH4NO3)
Ammonium nitrate salt is a combination product of NH3 and nitric acid HNO3. It includes the following outstanding physical and chemical properties:
Chemical formula: NH4NO3
Physical properties:
-
Ammonium nitrate NH4NO3 normally exists in the form of colorless transparent crystals. However, it can also exist as a white powder under conditions of room temperature and standard pressure.
-
Completely soluble in water and easily decomposed at high temperatures.
Chemical properties:
For example:
NH4NO3 → NH3 + HNO3 (at a temperature of 110 degrees Celsius)
NH4NO3 → N2O + 2H2O (at temperature 185 – 200 degrees Celsius)
2NH4NO3 → 2N2 + O2 + 4H2O (at a temperature of 230 degrees Celsius)
4NH4NO3 → 3N2 + 2NO2 + 8H2O (at a temperature of 400 degrees Celsius)
Calcium nitrate salt Ca(NO3)2
Next, let’s learn about calcium nitrate salt – one of the typical nitrate salts.
Chemical formula: Ca(NO3)2
Physical properties:
-
Calcium nitrate salt is a colorless inorganic compound that absorbs moisture from the air.
-
Melting temperature: 561 degrees Celsius (in anhydrous form) and 42.7 degrees Celsius in quadruple form.
-
Boiling temperature: Self-decomposition (in anhydrous form) and 132 degrees Celsius in quadruple form.
-
Ca(NO3)2 is soluble in ammonia but insoluble in nitric acid; Soluble in ethanol better than methanol.
Chemical properties:
-
The decomposition reaction produces calcium nitrite and oxygen.
-
Strong oxidizing properties when reacting with non-metals such as S, P,…
Exercises on nitrate salts in Chemistry Textbook Grade 11 with detailed explanations
So, we have learned all the basic theories surrounding nitrate salts. Please apply the knowledge you have learned to practice some basic exercises about nitrate salts in Textbook 11 below.

Solve problem 4 page 45 Chemistry 11 textbook
a. In the chemical equations of the pyrolysis reaction of iron (III) nitrate, what is the sum of the coefficients?
A. 5
B. 7
C. 9
D. 21
b. In the chemical equation of the pyrolysis reaction of mercury (II) nitrate, what is the sum of the coefficients?
A. 5
B. 7
C. 9
D. 21
Solution:
a. Answer D
Equation of pyrolysis reaction
4Fe(NO3)3 → 2Fe2O3 + 12NO2 + 3O2 (temperature)
b. Answer A
Equation of pyrolysis reaction
Hg(NO3)2 → Hg + 2NO2 ↑ + O2 ↑
Note: Nitrate salt pyrolysis reaction
-
Nitrate salts of highly active metals (K, Na…) are decomposed to form nitrite salts and O2.
-
Nitrate salts of metals Mg, Zn, Fe, Cu, Pb…. decomposed to form corresponding metal oxides, NO2 and O2-.
-
Nitrate salts of Ag, Au, Hg… decompose to form the corresponding metals, NO2 and O2.
Solve lesson 5 Chemistry 11 textbook page 45
Write the chemical equation for the reaction that carries out the following conversion series:
NO2 (1) → HNO3 (2) → CU(NO3)2
(3) → Cu(OH)2 (4) → Cu(NO3)2
(5) → CuO (6) → Cu (7) → CuCl2
Solution:
(1) 4NO2 + O2 + 2H2O → 4HNO3
(2) 8HNO3 + 3Cu → 3Cu(NO3)2 + 2NO↑ + 4H2O
Or CuO + 2HNO3 → Cu(NO3)2 + H2O
(3) Cu(NO3)2 + 2NaOH → Cu(OH)2↓ + 2NaNO3
(4) Cu(OH)2 + 2HNO3 → Cu(NO3)2 + 2H2O
(5) 2Cu(NO3)2 → 2CuO + 4NO2↑ + O2↑
(6) CuO + H2 → Cu + H2O (temperature)
(7) Cu + Cl2 → CuCl2 (temperature)
Solve lesson 6 Chemistry grade 11 Textbook page 45
When dissolving 30.0g of copper and copper (II) oxide mixture in 1.5 liters of 1.00M nitric acid solution (dilute), 6.72 liters of nitrogen monoxide (standard conditions) are released. Determine the percentage content of copper (II) oxide in the mixture, the molar concentration of copper (II) nitrate and nitric acid in the solution after the reaction, knowing that the volume of the solutions does not change.
Solution:
n(HNO3) = 1.5. 1.00 = 1.50 (mol)
n(NO) = 6.72/ 22.4 = 0.3(mol)
PTHH:
3Cu + 8HNO3 → 3Cu(NO3)2 + 2NO + 4H2O (1)
CuO + 2HNO3 → Cu(NO3)2 + H2O (2)
According to equation (1), n(Cu) = 3/2 xn(NO) = 3/2 x 0.3 = 0.45 mol
Let n(CuO) = y mol
We have: m(mixture) = m(Cu) + m(CuO) = 0.45 x 64 + 80y = 30.00
⇒ y = 0.015 ⇒ n(CuO) = 0.015 mol ⇒ m(CuO) = 0.015. 80 = 1.2g
(Or m(CuO) = 30 – 0.45 x 64 = 1.2g)
%CuO = 1.2/30 x 100% = 4%
According to equation (1), n Cu(NO3)2 = nCu = 0.45 mol
According to equation (2), n Cu(NO3)2 = n(CuO) = 0.015 mol
⇒ Total nCu(NO3)2 = 0.45 + 0.015 = 0.465 mol
CM(Cu(NO3)2 = 0.465/ 1.5 = 0.31 (M)
According to pt(1) n(HNO3) = 4 xn(NO) = 4 x 0.3 = 1.2 mol
According to pt(2) n(HNO3) = 2 xn(CuO) = 2 x 0.015 = 0.03 mol
Excess n(HNO3) = 1.5 – 1.2 – 0.03 = 0.27 mol
CM HNO3 = 0.27/ 1.5 = 0.18 (M)
Hopefully, through the above knowledge, readers will clearly understand what nitrate salt is, how to apply nitrate salt, and master nitrate salt exercises from basic to advanced. Don’t forget to visit Nguyễn Tất Thành every day so you don’t miss other interesting lessons about Math, Physics and Chemistry! Wishing you an effective learning process.
Nguồn: https://truongnguyentatthanh.edu.vn
Danh mục: Giáo dục



![[GIẢI ĐÁP] Chứng chỉ IELTS có được miễn thi tốt nghiệp không?](https://truongnguyentatthanh.edu.vn/wp-content/uploads/GIAI-DAP-Chung-chi-IELTS-co-duoc-mien-thi-tot-800x450.jpg)

